– “…We are currently in the second generation, specifically marked by the
advances in computer CPU technology. Advances in the third generation will allow for much of the diamond nano-skinned balloon systems to function. The fourth generation will converge networkability, energy conversion and molecular scale activities in atmospheric change”
The Smoking Man / November 21, 2018
Source – geopolitics.com
California Wildfire: Another Directed Energy Weapon Attack?
Here are some images of the aftermath of the California Wildfire. As you may notice, there’s a discrepancy between the still standing trees and the completely obliterated houses.
Here’s a similar situation from the recent past…
Was it caused by a directed energy weapon system [DEW], and for what purpose does it serve?
Will these series of geoweapon attacks force the Trump government to go back to the Paris Climate Accord?
The notorious MetaBunk site tried to smother any evidence-based analysis on similar events in the past…
But just below the comment section of that same debunker’s video, a certain SOBB3393 made the following comment:
Please explain how the fires started in the first place & why the roads are clear of debris, also explain why we don’t see any evidence of any porcelain in the videos of these fires. Also, please explain how a plastic garbage bin in the driveway of a leveled house is still in tact. Plastic wheelie bins aren’t wooden, so please explain this anomaly in another video.
As a firefighter & Fire Investigation Officer of 38+ years, I can honestly say I have never seen any fire behave like this, nor have I ever seen this type of fire aftermath .. I mean clean roadways? houses burnt to the ground where not even the toilet survives? Unheard of. Anywhere. Ever.
Something is very suspicious about these fires.” – SOBB3393
We can debate all day long, of course, but it is important to know that energy weapons do exist, and for how and when the technology is to be used is absolutely beyond our control.
Here’s an unclassified file taken directly from the US military website:
Operational Defenses through Weather Control in 2030
by
Michael C. Boger, Major, United States Air Force
A Research Report Submitted to the Faculty
In Partial Fulfillment of the Graduation Requirements
Advisor: Major Paul J. Hoffman
Maxwell Air Force Base, Alabama
April 2009
ABSTRACT
The United States needs to incorporate the defense against directed energy weapons with the same intensity used developing anti-ballistic missile defenses.
One of the major drawbacks to optical or directed energy systems is the inability to penetrate clouds or dense fog. Advances in technology are beginning to bring weather phenomena under our control. Greatly increased computing power and micronized delivery systems will allow us to create specific perturbations in local atmospheric conditions. These perturbations allow for the immediate and lasting ability to create localized fog or stratus cloud formations shielding critical assets against attack from energy based weapons. The future of nanotechnology will enable creation of stratus cloud formations to defeat DEW and optically targeted attacks on United Sates assets.
The solution the weather control problem involves networked miniature balloons feeding and receiving data from a four-dimensional variation (4d-Var) computer model through a sensor and actor network. A network of diamond-walled balloons enters the area to be changed and then both measures and affects localized temperature and vapor content. This system effectively shortens the control loop of an atmospheric system to the point it can be managed. The capabilities in the diamond-walled balloons are
based on the future of nanotechnology.
…
By creating clouds in specific locations and altitude blocks, optical
weapons systems will be forced to occupy predictable locations making them easier to target or avoid. Making the tracking laser and weapon the same thing reduces weapon time of flight and
is a critical capability of DE.
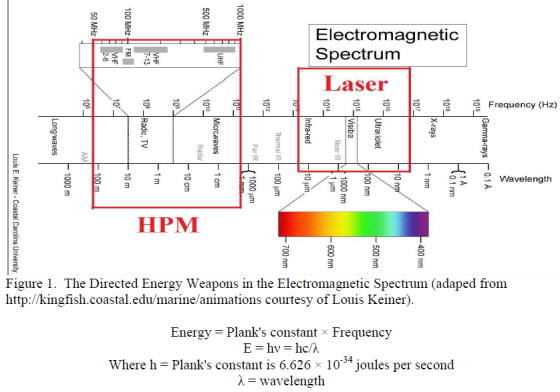
Directed Energy Weapons
High Energy Lasers (HEL) and High Power Microwaves (HPM) are currently the primary methods of directed energy attack. Both of these categories break down further into the methods of creating the laser or microwave energy as well as transmission and control of the
beams. It is the expectation that within the next 15 years, these types of DEW will become increasingly common on the battlefield.15
Department of Defense (DOD) interest in directed energy programs spans from the tactical to strategic uses on the ground and in space.16
HEL and HPM technologies have different methods of effectiveness on their target. HELs apply high temperatures on the surface, destroying their target. Lasers can also cause disorienting effects on
the operator of their target.17 HPMs affect the internal circuitry of the target or internal tissues of the operators.18
Both HELs and HPMs have the strengths of zero time of flight but the effects require a great deal of energy to remain coherent from the weapon to the target. HEL and HPM require separate discussion of effects and defeat mechanisms. DEWs have a limit of operation within the electromagnetic spectrum. The power of these weapons depends on their electromagnetic signature.
Figure 1 shows where laser and microwave weapons inhabit the electromagnetic spectrum.
Both wavelength and frequency are AU/ACSC/BOGER/AY09
tied together since the speed of the energy weapon is considered to be constant at the speed of light (c). As a result, the variables of wavelength or frequency are characteristics that can be modified. The amount of energy per second, measured as watts, depends on the pulse length or total amount of lasing or radiating time for a given beam. As frequency increases, wavelength decreases and the amount of energy in a directed beam also increases.
AU/ACSC/BOGER/AY09
The size of these predicted elements only depend s on the frequency of measurement and number of data points available in the given system.
The WRFM does not look at the global system, it does accurately simulate the internal and intrasystem physics of clouds. 51 So why can’t the weatherman get it right?
The availability of the WRFM and the computing power to support it are limited. The WRFM is a collaborative operation between
the NOAA, NCAR and six other major organizations. The WRFM is mostly used for research and future forecast method modeling.
Getting the proper amount and timeliness of data in to the WRFM is the weatherman’s limitation.
Most radar and satellite measurement methods take samples of portions of a weather system. Updating and maintaining a
persistent stream of system data from distinct points in the system
simultaneously is difficult. Most current methods of measurement are very capable of describing portions of a weather system by their movement or change. This method of mass flux element measurement works well with linear models; inputs are proportional to outputs. The non-linear modeling requires for selective use of data.
For better data assimilation and utilization, the measurement devices almost need to be a part of the weather system, and this is where
technology will fill the gap. The fast modeling and computations of the WRFM are now hindered by the accuracy of measuring in the sy
stem. How does one go from taking accurate forecasting to the actual development of a weather system?
Foundations of Weather Control
Relevance Tree
Relevance trees helps break a concept down to basic functions and requirement. For weather control, these topics further devolve into the physical or operational parts of a system to create a cloud in the atmosphere. The relevance tree was used as a tool to determine what
AU/ACSC/BOGER/AY09 technologies need to be linked in order to control a complex system like weather. Through collaboration between experts in weather, computer modeling, and nanotechnologies, the elements of the system are reduced from requi
red functions to the suggested components for weather creation.
The concept relevance tree (Appendix A) presents cloud development requirements with some additional considerations. Isolating and establishing the atmospheric area to be modified became the initial area of discussion among members of the Weather Modification Association and subject matter experts (SMEs). The concept tree indicated a grand set of ten major criteria:52
- Establish/Isolate a System
- Measure Variables in System
- Determine Required Variable Values in the System
- Change Variables in the System
- Network System Components
- Control Location of Components
- Deconfliction With other Assets
- Manpower
- Side Effects
- Vulnerability to Attack
(Weather Modification Association panel of experts and the author, 2008)
The size of the problem required the researcher to focus the problem to just accomplishing the development of a cloud system. As a result, items eight through ten were removed from this project. Manpower, possible side effects and vulnerability of the weather control system are important but were found to be beyond the scope of this project.
The remaining items were further broken down to the descriptions of their function. Great consideration was given to the difficulty of isolating the atmosphere for modeling. Debate and expert input settled the issue to broad effects stabilizing the mass flow to manageable levels in which the elements within the mesoscale could be affected would suffice. The concept relevance tree has been broken down to the critical requirements of isolating an atmospheric area; measuring and setting variables within the system. 18
AU/ACSC/BOGER/AY09
A closed loop system needs to be developed to control weather. Weather control goes one step further than the current capabilities of 3d-Var modeling while measuring atmospheric variables outside the system.
Two major technological humps stand in the way of weather
control. First, making a cloud in a specified geographic area requires setting and isolating a system to create weather in. Much like “controlling the air mass” with an air conditioner.
Second, the actual methods of altering the temperature, pressure, or vapor content within the elements of the system.
The Ideal Gas Law, PV=nRT is an extremely simplistic way of regarding the control of weather. Water vapor content changes this from an ideal gas equation, but sufficiently models the interaction. Cloud development depends on vapor content and method of coalescing into an opaque cloud.
Pressure X Volume = Quantity (moles) X Gas constant X Temperature
PV = nRT
Condensation rate is proportional to vapor condensation based on the Ideal Gas Law. It is the iterative and complex interaction between the equilibrium of condensation and the Ideal Gas Law that will develop clouds. Volume, in this case, depends on mass flow rates. Pressure and temperature are dependent on each other and the water content in the air will determine at what temperature/pressure a cloud will form. The nuclei of cloud formations can vary from water
droplets to micro ice-crystals. The change in pressure and temperature with altitude determine the construct of that mixture.
How do you control the inputs and outputs to your system?
I Give You Nanotechnology!
The component relevance tree (Appendix B) matched the requirements. Cross-referencing the requirements with the envir
onmental scan of future nanotechnology and AU/ACSC/BOGER/AY09 computer modeling provided solutions to the concept relevance tree. The primary problem determined through the relevance diagram was speed and precision at which a closed-loop
weather control system could operate. Nanotechnology enabled sensors and networks answered the problems of measuring, altering and communicating the variables within a weather system.
4d-Var modeling combined with current computing power and accurate data accounted for the control of the system. The delivery of these systems can be accomplished with current technology. Having the sensors, network and means of modification of the atmosphere part of the proposed cloud system removes control lag.
The center of this weather control system revolves around a formation of diamond nano-skinned balloons encasing a host of
nanomachines.
Current weather modification research focuses on the new concept of determining critical optimal perturbations in atmospheric conditions that will, in essence “box in” a volume of airspace. 53
The area of interest does not need to have zero mass flow. The flow only needs to be stabilized and directional enough to allow for modification of temperature, pressure and vapor content to the degree that it results in cloud formations. Perturbations can be as simple as heating or cooling a large area of atmosphere.
Large space-based reflectors could quickly generate a large high pressure area. The perturbation does not need to be as specific as building a cloud system and may be hundreds of miles away from the area of interest. 54
Once these designed blockades are in effect, the air mass that has been stabilized can then be adjusted. This is similar to using smoke in test section of a wind-tunnel. The flow only needs to be constant
and directional enough for the smoke added to allow for visualization of aerodynamic effects inthe tunnel test section.
Micro and nanotechnology provide both a detailed sensor grid to measure critical variables in a weather generation algorithm and then
fill in the variables required to generate the 20AU/ACSC/BOGER/AY09 desired effects. Current computer power enables 4d-Var modeling. Computing power in 2020 will enable the networking and sensor grid required 4d-Var analysis to determine variable
settings to establish these perturbations to control the system. 55
4d-Var extrapolates on the capabilities of WRFM 3d-Var analysis and determines the minimum large scale perturbation necessary. 56
The modeling starts with small initial state perturbations and simulates the nonlinear response over a 6 or 12 hour window. 57
Future applications of these perturbations take the form of isolated low and high pressure areas or troughs to steer the jet stream or its affect in relation to the area of interest. Making the high or low pressure area can be as simple as heating or cooling a massive column of air with diamond balloons. 58
Experiments on 4d-Var modeling began in 2002, already capable of
handing weather control data. Dr. Hoffman of Atmospheric and Environmental Research Incorporated a nd the former NASA Institute for Advanced Concepts (NAIC), denies that weather is a tr
uly chaotic system when modeled through 4d-Var methods. 59
Once the mass flow into and out of an area is controlled, it becomes a simple issue of establishing specific localized temperature (dew
point spread), pressure gradient and water content per volume of air through a column in the atmosphere. Dr. J. Storrs Hall provided a
solution to half of the concept relevance tree through insight on diamond nano-skinned balloons.
The component tree helps indicate now nanotechnology will enable diamond nano-skin balloons to accomplish several tasks. Dr. Hall
best describes the diamond balloons.
“You build a little balloon, my guess is the balloon needs to be somewhere between a millimeter and a centimeter in size. It has
a very thin shell of diamond, maybe just a nanometer thick. It is round, and it has inside it an equatorial plane that is a mirror. If you
squished it flat, you would only have a few nanometers thick of material. Although you could build a balloon out of materials that we build balloons out of now, it would not be economical for what I’m going to use it for.” 60
AU/ACSC/BOGER/AY09
Motion, location and networking of the balloons can be controlled in several ways.
Altitude is controlled through the buoyancy of the balloon through a combination of electrolysis of water and nano-pumps removing molecular water from within the balloon. The walls of the balloon could have nano-fans, providing additional thrust. 61, 62
Utilization of the earth’s magnetic field and the charge on the skin of the balloons themselves will aid in formation keeping with other balloons. 63
Nano-network controllers within each balloon will maintain contact with neighboring balloons. Solar power through the nano-antenna arrays will charge nano-batteries. 64
Proton exchange membrane (PEM) batteries are current day nanotechnology that is powered by electrolysis of water. 65
Directional micro-antenna will be able to determine position of the balloons with the formation relative to one another. The diamond balloons will house an array of sensor and communication technology which is currently being developed to build radios from carbon nanotubes. 66
These communication systems collect and transmit onsite, accurate data to the complex computer systems that model and establish the controls for a weather system. Some of the larger balloons function as a node, housing a GPS receiver 67 and micronized network uplink to provide high frequency communication of the network to a ground
station or UAV.
The distribution of these balloons will depend on the amount of atmospheric mass flow in the AOR. Discussions with WMA participants and Dr. Hall estimate at least one to two balloons per cubic meter would be required to initiate changes in conditions. These estimates were based on current cloud seeding densities. Networking these balloons is similar to current research into nano-swarms.
The study of sensor and actor networks (SANET) encompasses the communication, control and activity of our proposed balloon network. Such a network concept includes the requirement to maneuver nodes and communicate in a complex and distributed network.
The study of self controlling and communicating networks began in the 1960s.
The concept AU/ACSC/BOGER/AY09 accelerated within the last five years with the spread of integrated wireless networking. 71 The function of SANETs specifically requires a network of sensors to communicate, maintain positional distribution and sense among a distribution of nodes.
These nodes then pass the datato and from a monolithic processing center, our 4d-Var model in this case. SANETs are currently limited by architecture and power, but are already being developed.
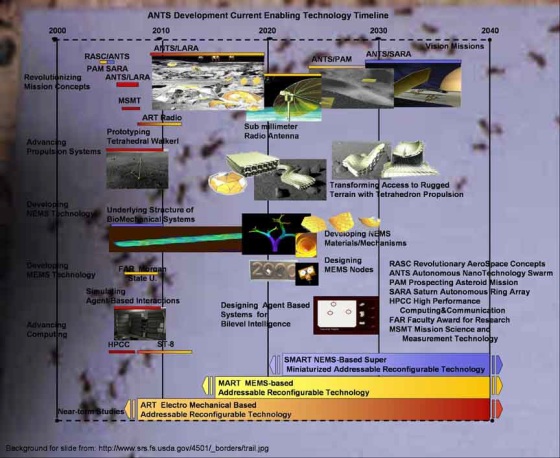
The weather control application of such networks follows the development timeline and technology of Autonomous Nanotechnology Swarms.
Figure 2. Autonmous NanoTechnology Swarms (ANTS) Development Timeline (reprinted from http://ants.gsfc.nasa.gov/time.html). Autonomous NanoTechnology Swarms (ANTS) is currently being researched by Goddard Space Flight Center.
Modeled after insects, ANTS is network architecture applicable to future nanofactories. Goddard Space Flight Center is currently using ANTS beginnings in experiments 23 AU/ACSC/BOGER/AY09
with large scale robot “herds.” ANTS is the support structure for Addressable Reconfigurable Technology (ART). The core of ART is a networked swarm of nano machines capable of configuring themselves for a variety of tasks.
The element control requirements for ARTs are nearly identical to what is required for the proposed network of nano-enabled balloons for weather sensing and control. The timeline of ANTS development in Figure 2 indicates usable functionality for distributed SANET control by 2030.
The individual methods of atmospheric modification at the molecular level share development with the capabilities of nanomachines. A combination of nano-pumps working at the molecular level can transport water between layers in the atmosphere as the balloons bob up and down in the air column.
Nanofactories can conduct electrolysis on water, molecularly
building nuclei of droplets or ice crystals or reducing water vapor. Cooling through thermoelectric nanomaterials currently being de
signed for computer applications will enable control of the balloon skin temperature.
This cooling and vapor content will have an effect on the localized pressure as a result of the ideal gas law. As with many non-linear systems, small inputs can develop large and self sustaining events, as determined by a 4d-Var model. Larger, more temperature based control balloons will be the center of the high and low pressure
perturbations. The effect required is not as specific, resting mostly on regional temperature.
Will nanotechnology be developed to the level of atmospheric control by 2030?
Money spent on nanotechnology gives a good indication if it will continue to develop.
Lux Research, a market science and economic research firm, claims that nanotechnology will become commonplace in across the spectrum of consumer goods by 2014.
2004 showed a mere 12 million dollars invested globally in
nanotechnology. In contrast, 2008 Lux Research estimates rise to 150 billion in sales of emerging nanotechnology. It is expected that sales of nanotechnology will reach 2.5 trillion dollars by 2014.
Dr. Hall, stated that “2030 nanotech is 24 AU/ACSC/BOGER/AY09
likely to be good enough for a Weather Machine” in correspondence with the researcher.
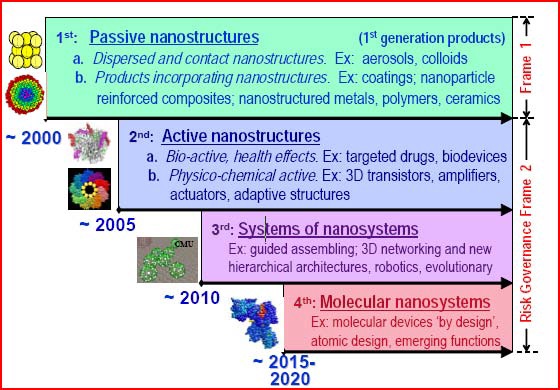
Four generations of nanotechnology have been described by the U.S. National Nanotechnology Initiative (Fig 3).
We are currently in the second generation, specifically marked by the
advances in computer CPU technology. Advances in the third generation will allow for much of the diamond nano-skinned balloon systems to function. The fourth generation will converge networkability, energy conversion and molecular scale activities in atmospheric change.
Nanotechnology enables the two critical humps in weather control. By the 2030 timeframe, nanotechnology will allow complex models to receive accurate and timely data from within and across the atmospheric system. These models can then direct those elements to make changes to the atmospheric system. System detail, data and response will be a function of the size of an area, how quickly it is changing and how many weather balloons are at your disposal…
Read Full Article…https://geopolitics.co/2018/11/14/california-wildfire-another-directed-weapon-attack/