Picture this: A billion-ton coronal mass ejection (CME) slams into Earth’s magnetic field. Campers in the Rocky Mountains wake up in the middle of the night, thinking that the glow they see is sunrise. No, it’s the Northern Lights. People in Cuba read their morning paper by the red illumination of aurora borealis. Earth is peppered by particles so energetic, they alter the chemistry of polar ice.

Hard to believe? It really happened–exactly 160 years ago. This map shows where auroras were sighted in the early hours of Sept. 2, 1859:
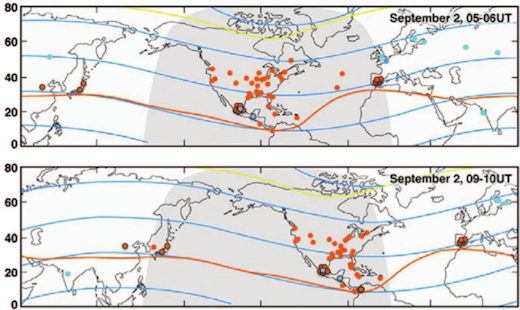
As the day unfolded, the gathering storm electrified telegraph lines, shocking technicians and setting their telegraph papers on fire. The “Victorian Internet” was knocked offline. Magnetometers around the world recorded strong disturbances in the planetary magnetic field for more than a week.
The cause of all this was an extraordinary solar flare witnessed the day before by British astronomer Richard Carrington. His sighting on Sept. 1, 1859, marked the discovery of solar flares and foreshadowed a new field of study: space weather. According to a NASA-funded study by the National Academy of Sciences, if a similar storm occurred today, it could cause a trillion dollars in damage to society’s high-tech infrastructure and require years for complete recovery.
SOURCE: http://www.spaceweather.com/









